Table of Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Understanding User Story Map in Jira
- III. Establishing Effective Communication with Stakeholders
- IV. Collaboration Process Using User Story Map
- V. Managing Stakeholder Feedback with User Story Map
- VI. Continuous Communication and Updates
- VII. Advanced Tips and Tricks for Using User Story Map in Jira
- VIII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
Collaboration and communication with stakeholders are essential skills for project managers and team members. They help to ensure that the project meets the expectations and requirements of the stakeholders and that the project delivers value to them. One of the most effective tools for those demands is the user story map in Jira.
This article aims to show you how to use the user story map in Jira to collaborate and communicate with your stakeholders effectively. You will learn how to create a user story map, share it with your stakeholders, collect and incorporate their feedback, and update and maintain your user story map throughout the project lifecycle.
II. Understanding User Story Map in Jira
User Story Map explanation
A user story map in Jira provides a graphical visualization of the product backlog. It outlines the user’s journey through the product, from their tasks to their ultimate goals. Each product feature is captured in the form of a user story – a simple, concise description of a feature from the user’s perspective. The map aligns these stories along a horizontal axis representing the user journey, with different activities or tasks marked along the way. This structure helps visualize the product’s functionality and maintains a focus on the user’s experience.
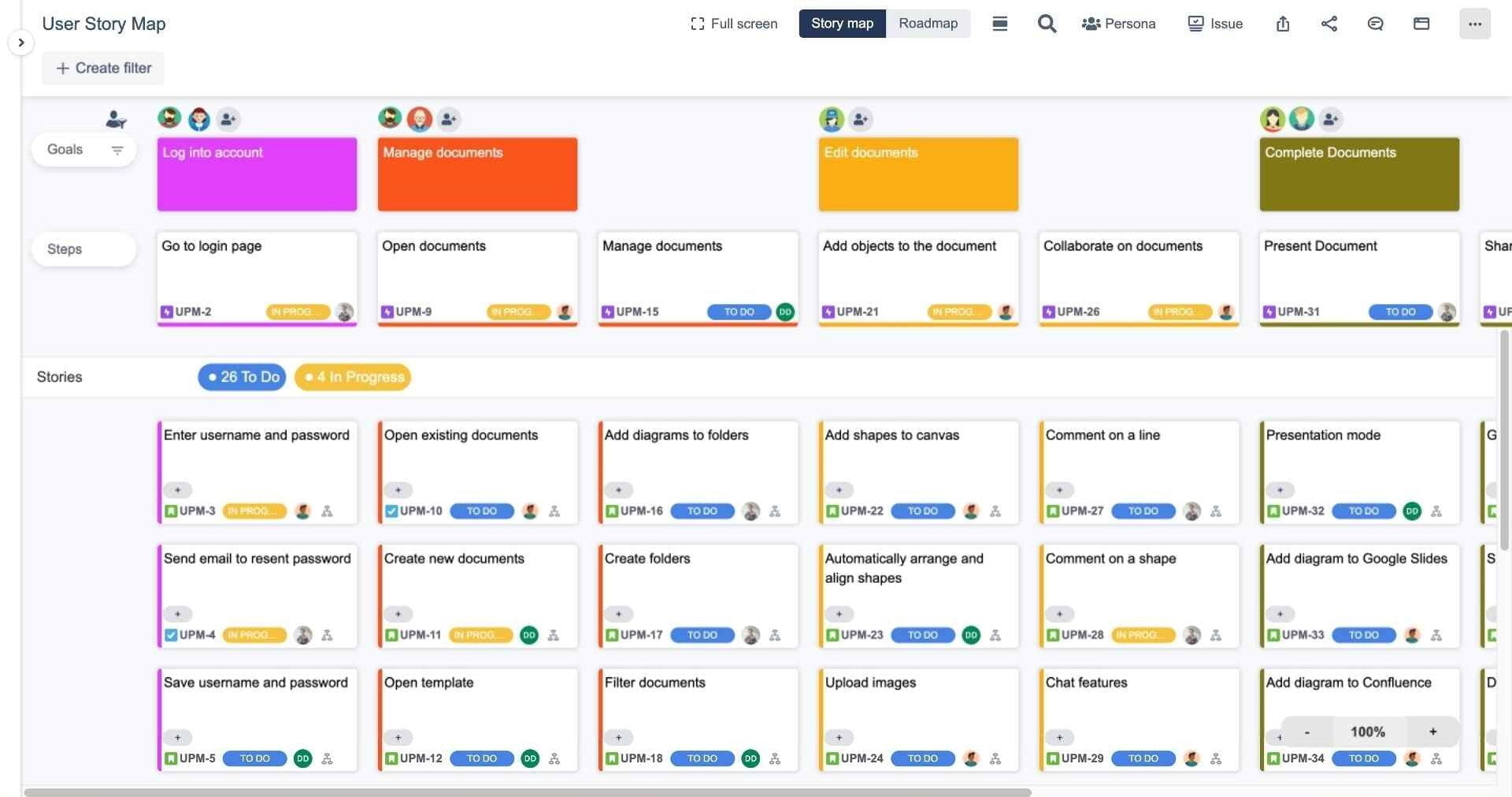
Key Components of a User Story Map in Jira
A user story map in Jira consists of several key components:
- User Activities/Goals: These are high-level tasks or actions users undertake when interacting with the product. They form the topmost layer of the story map.
- Epics: These are larger bodies of work that group together related user stories. They provide a broad understanding of the requirements and help track progress.
- User Stories: These are the product’s specific features, each described from the user’s perspective. They form the second layer under the user activities and are what the team will work on during development.
- Versions/Releases: This component refers to the specific releases in which the completed user stories will be delivered. It helps manage and communicate the delivery schedule to stakeholders.
- Story Status: This tracks the progress of each user story, whether it’s yet to be started, in progress, or completed.
Benefits of Using a User Story Map
Utilizing a user story map in Jira offers several benefits:
- User-Centric Focus: By visually mapping the user’s journey, the story map helps ensure the development process remains user-centric, improving the final product’s usability and relevance.
- Improved Prioritization: By visualizing the hierarchy of user activities and stories, the map helps teams prioritize tasks based on their value to the user.
- Enhanced Collaboration and Communication: The visual nature of the story map makes it an excellent tool for discussion, helping stakeholders understand the product scope and development status at a glance.
- Flexible Planning: The story map’s structure allows for easy adjustments, facilitating agile planning and helping teams adapt to changes or new information.
- Increased Transparency: The story map provides stakeholders with a clear view of what the team is working on, promoting transparency and trust.
III. Establishing Effective Communication with Stakeholders
Identifying Stakeholders
Before effective communication can occur, it’s essential to identify who the stakeholders are for your project. They could be internal stakeholders, like your organization’s team members, management, and other departments. External stakeholders include clients, investors, partners, suppliers, or regulatory bodies. Understanding each stakeholder’s interests, expectations, and influence over the project will aid in shaping your communication strategy.

Importance of Clear and Effective Communication with Stakeholders
Clear and effective communication with stakeholders is pivotal for the success of any project. It ensures everyone involved understands the project goals, their roles and responsibilities, and the progress towards these goals. Effective communication reduces the potential for conflict, boosts stakeholder engagement, and helps to manage expectations. Moreover, it facilitates decision-making, enables faster problem resolution, and promotes a positive project environment.
Strategies for Successful Communication
- Understand Stakeholder Needs: Each stakeholder may have different information needs. Understand these needs and tailor your communication accordingly.
- Use Appropriate Communication Channels: Use the proper channels to communicate with stakeholders. This could be through email, meetings, project management tools like Jira, or a combination.
- Regular Updates: Keep stakeholders informed about the project’s progress regularly. Use the user story map in Jira to visually communicate what’s been completed, what’s in progress, and what’s next.
- Encourage Feedback: Make it easy for stakeholders to provide feedback. This could be done through regular meetings, surveys, or dedicated feedback channels in Jira.
- Transparent and Honest Communication: Be open about project successes and challenges. Transparency builds trust and enables stakeholders to make informed decisions.
- Proactive Communication: Don’t wait for stakeholders to ask for information. Proactively communicate important updates, changes, or issues.
- Effective Listening: Effective communication is not just about talking; it’s also about listening. Pay attention to stakeholders’ feedback, concerns, and suggestions. This will make them feel valued and improve your working relationships.
IV. Collaboration Process Using User Story Map
Steps to create a user story map in Jira
Read this blog to learn more about the story map and how to create a user story map in Jira with ProductGo: ProductGo Basic #3: How to use User Story Map by ProductGo
Find out about how ProductGo works with your Jira here: Agile User Story Maps, Roadmaps & Persona for Jira.
Illustrating How to Involve Stakeholders in the Process
Stakeholders can be involved in various stages of creating and maintaining the user story map.
- Brainstorming: Invite stakeholders to brainstorming sessions when identifying user activities and creating user stories. Their diverse perspectives can enrich the user story map.
- Prioritization: Seek stakeholders’ inputs when prioritizing user stories. They can provide valuable insights into the most critical features from their viewpoint.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular review meetings with stakeholders to discuss the user story map’s progress. Here, they can provide feedback and suggest changes if necessary.
- Updates: Use Jira to provide stakeholders with real-time updates on the project’s progress.
Addressing Common Issues and Solutions in the Collaboration Process
Collaboration can come with its challenges. Here are some common issues and potential solutions:
- Issue: Disagreements on priorities.
Solution: Hold a collaborative session with stakeholders to discuss and agree on prioritizing user stories. - Issue: Stakeholders feeling disconnected from the project.
Solution: Regular updates and involvement in decision-making can help stakeholders feel more connected to the project. - Issue: Misunderstanding or lack of clarity about project goals.
Solution: Regularly revisit and communicate the project goals using the user story map.
Remember, communication, understanding, and mutual respect are the key to effective collaboration.
V. Managing Stakeholder Feedback with User Story Map
Document Stakeholder Feedback in Jira
Jira offers several options for documenting stakeholder feedback. This can be done through comments on specific user stories, creating new tasks based on the feedback, or even leveraging Jira’s issue-tracking features. Here are some steps to follow:
- Create a Dedicated Issue: If feedback requires significant work or changes, create a new issue in Jira. This allows for tracking the work associated with the feedback.
- Use Comments: For minor changes or discussions, use the comments section. This can be done directly on the relevant user story.
- Use Labels: Create labels to categorize feedback. This helps to track and organize feedback systematically.

Incorporate Feedback into the User Story Map
Incorporating stakeholder feedback into the user story map can be done through several steps:
- Evaluate the Feedback: Not all feedback will result in changes. Evaluating the feedback in the context of the project goals and user needs is crucial.
- Update User Stories: If feedback suggests a change in a specific feature, update the relevant user story. This could involve editing the description or changing the prioritization.
- Add New User Stories: Some feedback may introduce new ideas. In this case, please create a new user story and fit it into the existing map.
- Revisit Prioritization: Feedback may alter the importance of specific user stories. Revisit the prioritization of user stories if needed.
- Update Stakeholders: Once changes are made based on feedback, update the stakeholders about the changes and their impact on the project.
Manage Conflicting Feedback from Different Stakeholders
Conflicting feedback can pose a challenge in project management. Here’s how you can handle such situations:
- Clarify the Feedback: First, ensure you understand the feedback from each stakeholder. Misunderstandings can sometimes lead to perceived conflicts.
- Facilitate a Discussion: Arrange a meeting with the conflicting parties to discuss the feedback. Open conversation can often lead to compromise or new solutions.
- Prioritize Based on Project Goals: Refer to the project goals when resolving conflicts. The feedback that aligns most with these goals should take precedence.
- Seek Third-Party Opinion: If the conflict persists, seeking a third-party opinion or mediator could provide a new perspective.
- Document the Outcome: Document the conflict and decision regardless of the result. This provides a reference for future disputes and maintains transparency with stakeholders.
VI. Continuous Communication and Updates
Importance of Maintaining Ongoing Communication with Stakeholders
Maintaining ongoing communication with stakeholders is critical to ensuring a project’s success. Regular communication informs stakeholders well about the project’s progress, reduces uncertainty, and helps manage expectations. It’s also an opportunity to gather feedback and address any concerns or issues that may arise. Furthermore, open and ongoing communication enhances stakeholder engagement, promotes transparency, and fosters a collaborative environment.
Using Jira to Provide Regular Project Updates to Stakeholders
Jira is a powerful tool for facilitating ongoing communication with stakeholders. Here’s how you can leverage its features:
- Project Status Updates: Use Jira’s dashboard to share high-level project status updates. This can include overall project progress, completed tasks, upcoming tasks, and any issues or blockers.
- Detailed User Story Updates: For more detailed updates, share specific user stories. This can include the story’s status, who’s working on it, any comments or discussions about it, and its due date.
- Automated Notifications: Jira lets you set up automatic notifications for different actions. This way, stakeholders can receive immediate updates when a user story changes status, a new comment is added, or changes to the project timeline.
- Reports and Charts: Use Jira’s reporting features to share detailed progress reports, burn-down charts, and other visual representations of project data.
Leveraging the User Story Map for Ongoing Discussions and Updates
A user story map is a living document that evolves as the project progresses. It serves as a visual guide to the project, making it an excellent tool for ongoing discussions and updates.
- Updating the Map: As the user stories progress, update their status on the story map. This provides a visual update on what’s been done, what’s being worked on, and what’s next.
- Facilitate Discussions: The user story map can be used to facilitate discussions during meetings with stakeholders. It can help address questions, clarify understanding, and assist decision-making processes.
- Soliciting Feedback: The user story map can also solicit stakeholder feedback. Ask for their input on prioritizing user stories, potential improvements, or new user stories to be added.
- Review Meetings: Conduct regular review meetings based on the user story map. In these sessions, walk through the map with stakeholders, discussing progress, challenges, and next steps.
VII. Advanced Tips and Tricks for Using User Story Map in Jira
Recommendations for Maximizing the Benefits of the User Story Map
- Include enough detail, but avoid over-complication: The user story map should be comprehensive, but it should also be easily understandable. Ensure that user stories are concise and clear, and avoid including too many details that could make the map difficult to navigate.
- Use color-coding: Color-coding user stories can provide additional information at a glance. You can use colors to denote priority, indicate different types of tasks, or identify tasks assigned to other team members.
- Regularly refine the map: The user story map is not static. As the project progresses and feedback is received, periodically refine and update the map.

Discussing the Integration of User Story Map with Other Jira Tools
The user story map is integrated with Jira tools to streamline project management:
- Jira Agile Boards: Sync the user story map with your Agile boards. Changes in one can reflect in the other, providing a consistent view across different project management tools.
- Jira Software: Integrate with Jira Software for more extensive project tracking capabilities. You can link user stories to specific issues in Jira Software, making it easier to manage the project.
Highlighting Potential Add-ons or Extensions to Enhance User Story Mapping Capabilities
ProductGo is a powerful tool that helps you create agile story maps, roadmaps, and portfolio boards for Jira. It allows you to visualize your product backlog, prioritize your features, plan your sprints, and track your progress. ProductGo helps you collaborate with your team and stakeholders, communicate your vision and deliver value to your customers.
This application is a Jira app that integrates seamlessly with your existing projects and issues. It enables you to create and edit story maps, roadmaps, and portfolio boards within Jira without switching to another tool or platform.
Find out about how ProductGo works with your Jira here: Agile User Story Maps, Roadmaps & Persona for Jira.
VIII. Conclusion
This comprehensive guide shows how to effectively collaborate and communicate with stakeholders using the user story map in Jira. The story map facilitates productive dialogue, decision-making, and project alignment by employing a user-centric focus, prioritizing tasks based on user value, and maintaining transparency. Moreover, continuously soliciting feedback and incorporating it into the user story map ensures our project evolves with stakeholders’ expectations and needs.
Leveraging Jira tools and extensions like ProductGo further enhances the user story mapping capabilities, providing a dynamic, integrated, and visual approach to project management. Understanding and employing the user story map in Jira forms the crux of a successful stakeholder collaboration strategy, fostering mutual understanding and respect and ultimately leading to a successful project.













1 Comment. Leave new
Complete information. Thanks for sharing your invaluable knowledge and experience.