In the dynamic world of product management, understanding and empathizing with your target audience is more than a necessity—it’s a strategic advantage. This comprehensive guide delves into the vital role of personas in product management.
Personas, semi-fictional characters that represent key segments of your target audience, are not just mere profiles but powerful tools that bring user-centricity into the heart of product development. They help product teams visualize and empathize with their end-users, ensuring that product features and functionalities truly resonate with user needs and preferences.
Table of Contents
- I. Understanding Personas in Product Management
- II. Why Personas are Crucial in Product Management
- III. Key Elements of Effective Personas
- IV. Creating Personas: A Step-by-Step Guide
- V. Best Practices in Persona Creation
- VI. Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Persona Creation
- VII. Enhance your Jira project user-centric with Personas by ProductGo
- Conclusion
I. Understanding Personas in Product Management
Within the sphere of product management, a persona is a semi-fictional character that embodies the key characteristics of a significant segment of a product’s target audience. Unlike a real individual, a persona is a composite archetype crafted from numerous users’ observed behavior, goals, needs, and motivations. Personas help product managers and their teams visualize the end-users, providing a clear, shared understanding of who they are designing and developing products for.
→ Try out Advanced Personas by ProductGo

Personas play a pivotal role in grounding product decisions in user-centricity. By bringing a human face to data and user research, personas enable teams to empathize with their users.
This empathetic approach ensures that product features, functionalities, and user experiences are aligned with the real needs and preferences of the users, rather than being based on assumptions or abstract data.
While personas and target demographics may seem similar, they serve different purposes. Target demographics provide a broad overview of a market segment, often in terms of age, gender, location, and socioeconomic status.
In contrast, personas delve deeper, providing a more nuanced view of the target users. They include behavioral traits, life context, goals, challenges, and attitudes. This depth makes personas more actionable for product development than the generalized view provided by demographics.
II. Why Personas are Crucial in Product Management
Enhancing Customer Empathy and Understanding
Personas are instrumental in fostering empathy within product teams. By representing users as real, relatable individuals, personas make it easier for teams to understand and prioritize the needs and challenges of their target audience.

Products designed with a deep understanding of the user’s life, emotions, and environment tend to be more intuitive, accessible, and ultimately, more successful in the market.
Tailoring Product Features to Meet User Needs
A well-crafted persona guides product managers in tailoring product features and functionalities to meet the specific needs of their users. By highlighting the user’s goals, pain points, and behavior patterns, personas help in identifying what features will be most beneficial and how they should function. This tailored approach ensures that the product solves real problems and enhances the user experience, leading to greater user engagement and satisfaction.
Improving Communication within Product Teams and with Stakeholders
Personas serve as a common language for discussing user needs across different teams and stakeholders. When everyone has a shared understanding of who the user is, communication becomes more efficient and focused. This alignment is crucial during the product development process, especially when making critical decisions or changes. Personas help ensure that these decisions are always made with the end user in mind.
III. Key Elements of Effective Personas
The elements of personas in product management are designed to provide a comprehensive and realistic representation of a target user segment. These elements help in creating a detailed and actionable profile that guides product development and decision-making. Here are the elements:
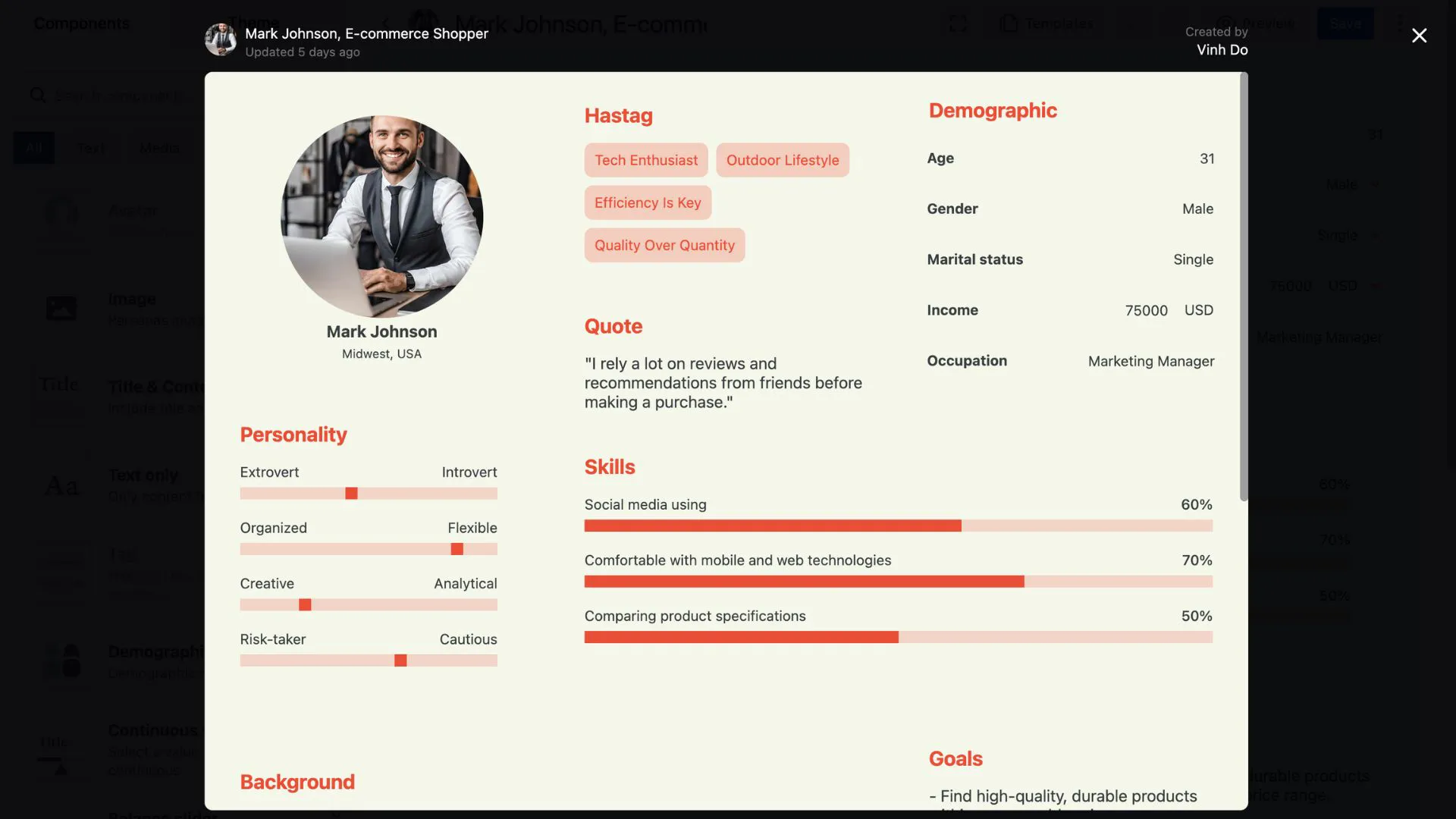
- Demographic Information: Age, gender, occupation, education, income.
- Psychographic Information: Attitudes, interests, personality traits, values, lifestyle.
- User Goals and Motivations: Objectives and aspirations related to the product and broader life or professional goals.
- Pain Points and Challenges: Problems or obstacles the persona faces that the product might address.
- Behavior Patterns: Typical behaviors, habits, and usage patterns related to the product.
- Technological Proficiency: The persona’s comfort and familiarity with technology.
- Preferred Communication Channels: How the persona prefers to receive information and communicate.
- Brand Interactions and Loyalty: Views and interactions with existing brands, including attitudes towards competitors.
- Visual Elements: A representative photo or illustration of the persona.
- Quotes and Anecdotes: Adding direct quotes or short stories based on user research can bring the persona to life and make them more relatable for the product team.
- Influencers and Decision Makers: Identifying who or what influences the persona’s decisions, especially in purchasing or using products.
Let’s dive into the important components:
Demographic Information
Demographic details form the basic foundation of a persona. This information includes age, gender, occupation, education level, and income. While these data points don’t provide deep insights into user behavior, they help in framing a general background of the persona.

Psychographic Information
Psychographic details add depth to personas, encompassing attitudes, interests, personality traits, values, and lifestyles. This information is vital for understanding the motivations, preferences, and decision-making processes of users.
User Goals and Pain Points
Understanding what the user aims to achieve with the product (goals) and the obstacles they face (pain points) is crucial. This insight guides the development of features and functionalities that directly address these aspects.
User Behavior Patterns
Behavior patterns include how users interact with similar products or services, their habits, and their decision-making process. This information helps in anticipating how a persona might use the new product and what features they would find most useful.

The Importance of Data in Persona Creation
Effective personas are grounded in real data and not just assumptions. This data can be gathered through methods like surveys, interviews, user testing, and analytics. The use of empirical data ensures that personas accurately reflect the target audience, making them more reliable for guiding product decisions.
IV. Creating Personas: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating effective personas is a crucial step in user-centered product development. This guide outlines a clear and concise process for developing personas that can help you better understand your users and their needs.
1. Gathering and Analyzing User Data
- Data Collection: Start by gathering data about your potential users. This can be done through surveys, interviews, user testing, and reviewing existing customer data.
- Analysis: Look for patterns in the data that reveal common characteristics, behaviors, and preferences among your users.
2. Identifying Patterns and Common Characteristics
- Segmentation: Divide your data into segments based on common characteristics. These could be based on user behavior, needs, goals, or demographics.
- Pattern Recognition: Identify trends within each segment that will inform the creation of your personas.
3. Developing the Persona Narrative
- Profile Creation: Use the identified patterns to create detailed profiles for each persona. Include demographic and psychographic information, goals, pain points, and typical behavior patterns.
- Narrative Development: Craft a narrative that brings each persona to life, making them relatable and realistic.
4. Validating and Refining Personas with Real Users
- User Feedback: Present your personas to real users or stakeholders for feedback. This helps ensure that your personas accurately reflect real user characteristics and needs.
- Refinement: Adjust your personas based on this feedback, refining them to better represent your target audience.
5. Tips on Visual Representation of Personas
- Visual Design: Create visual representations of each persona, such as photos or illustrations, to make them more engaging and memorable.
- Accessibility: Ensure that these visuals are clear and accessible, complementing the written persona profiles.
By following these steps, you can create personas that are not only accurate reflections of your target audience but also powerful tools for guiding your product development process.
V. Best Practices in Persona Creation
Creating effective personas is crucial for understanding and empathizing with users during product development. Here are some best practices to enhance the utility of personas:

Realism and Data-Driven Approach
- Realistic personas are grounded in actual user behaviors, needs, and demographics. Avoid creating fictional characters that don’t reflect your target audience.
- Data-driven personas rely on research, user interviews, and analytics. Collect quantitative and qualitative data to inform persona creation.
Regular Updates
- Personas should evolve alongside your product. Regularly update them based on new insights from user feedback, usability testing, and market trends.
- Consider changes in user behavior, technology, and industry shifts when revising personas.
Avoid Stereotypes and Biases
- Challenge assumptions and avoid perpetuating stereotypes. Be mindful of unconscious biases.
- Ensure personas represent diverse backgrounds, abilities, and experiences. Avoid reinforcing harmful stereotypes.
Integration into Product Development
- Integrate personas throughout the entire product lifecycle. Use them during ideation, design, development, and testing.
- Align personas with user stories, feature prioritization, and usability testing. Keep them accessible to the entire team.
Remember, personas are not static documents—they should evolve as your understanding of users grows.
VI. Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Persona Creation
Creating personas is a fundamental step in product management, but it’s important to be aware of common pitfalls that can diminish their effectiveness. Here’s a guide to the most common mistakes to avoid:
Creating Too Many Personas
- While personas are valuable, overloading your team with too many can be counterproductive.
- Focus on quality over quantity. Prioritize personas that represent significant user segments.
Relying on Assumptions Rather Than Data
- Assumptions can lead to inaccurate personas. Base them on solid research and user insights.
- Conduct interviews, surveys, and usability tests to gather reliable data.
Neglecting to Update Personas
- Static personas become outdated. Regularly refresh them with new information.
- Consider changes in user behavior, technology, and market trends.
Overgeneralization and Stereotyping
- Avoid creating personas that oversimplify or reinforce stereotypes.
- Represent diverse backgrounds, needs, and experiences.
Failing to Align Personas with Business Goals
- Personas should serve a purpose. Ensure they align with business objectives.
- Use personas to inform product decisions, prioritize features, and enhance user satisfaction.
By avoiding these pitfalls, you’ll create personas that truly drive user-centered design and contribute to the success of your product.
VII. Enhance your Jira project user-centric with Personas by ProductGo
Discover the enhanced Personas feature by ProductGo, an innovative addition to your Jira projects that brings a user-centric approach to life. Our revamped interface is clean, detailed, and incredibly user-friendly, designed for intuitive interaction and easy navigation.
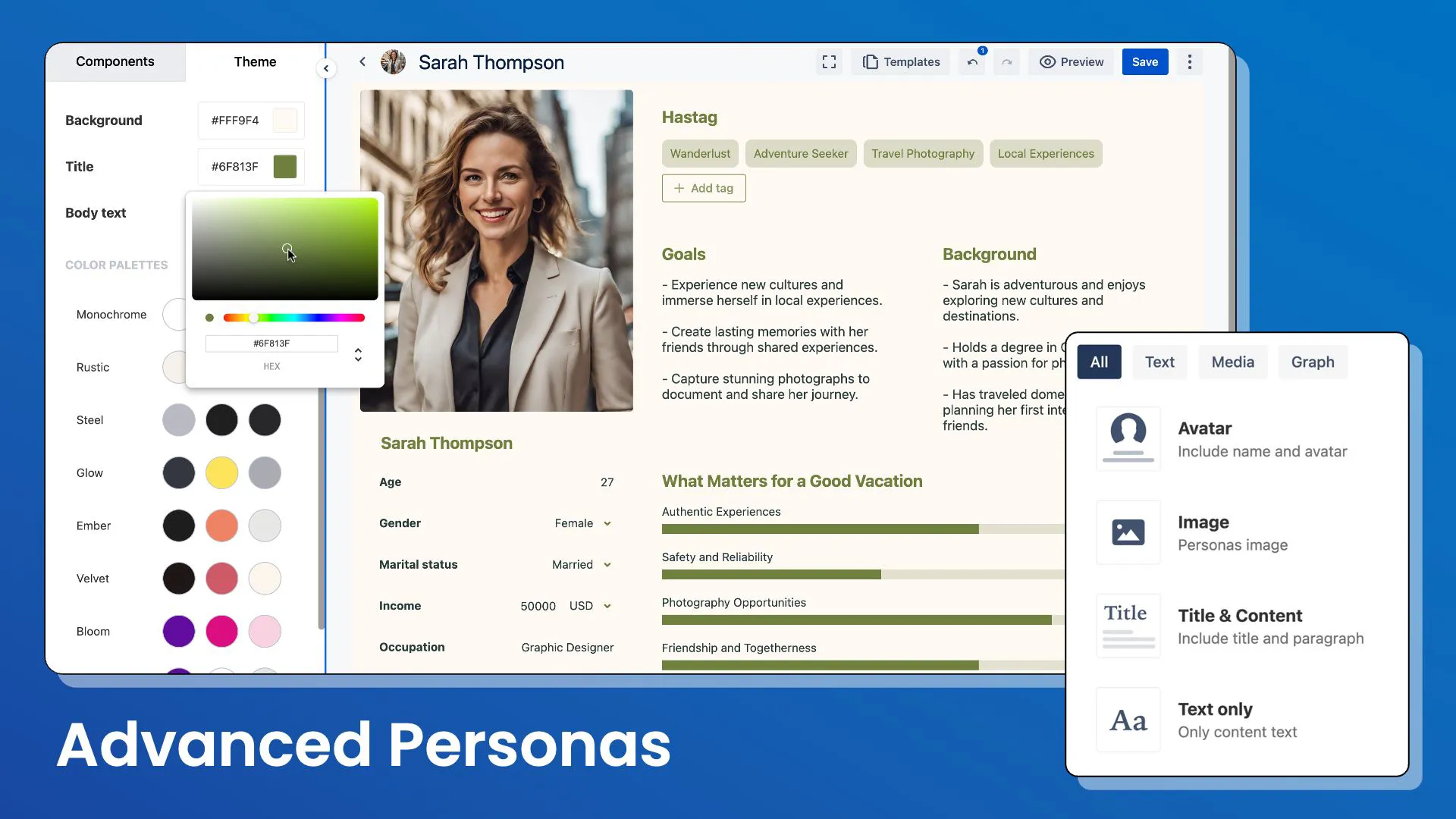
Centralize your persona management in one convenient location, eliminating the hassle of scattered data. This seamless integration allows for the efficient creation and management of both global and project-specific personas.
→ Try ProductGo now: Agile User Story Maps, Roadmaps & Persona for Jira
Enhanced accessibility puts personas at the heart of your projects, simplifying the process of viewing and creating user profiles. With our user-friendly design and diverse templates tailored for various industries, persona creation is now more effortless and intuitive.
Embrace the revolution in user-centric design with ProductGo’s Personas feature, transforming the way you understand and engage with your users.
→ Related content: ProductGo New Feature: Personas | December 2023
Conclusion
As we conclude this comprehensive journey through the world of personas in product management, it’s clear that personas are more than just profiles; they are the cornerstone of user-centric design. By integrating personas into every stage of the product development process, from ideation to execution, you ensure that your products are not only aligned with business goals but also deeply resonant with the needs and aspirations of your users.
Remember, the effectiveness of personas lies in their realism, continuous evolution, and integration into your product strategy. Whether you’re a seasoned product manager or new to the field, embracing personas will undoubtedly enhance your approach, leading to products that truly connect with your audience.
So, as you step forward in your product management journey, carry the insights and strategies shared in this guide, and let personas be your guide to creating more impactful, user-centered products.